大家好,我是大头,职高毕业,现在大厂资深开发,前上市公司架构师,管理过10人团队!
关注我发送“MySQL知识图谱”领取完整的MySQL学习路线。
MCP 在AI技术大火的当下,各个公司都在搞AI-Agent技术。对于Agent来说,其实还处于一个早期的阶段,没有所谓的最佳实践。更没有一些标准规则。可谓是一片蓝海。
大厂们也都在做着自己的一些尝试。但是总有人在建设底层规则。
MCP就是一个标准化的产物。它定义了一些标准。
Model Context Protocol(MCP)是由Anthropic于2024年11月推出的开放标准,旨在为大型语言模型(LLM)应用提供统一的上下文交互接口,使其能够与外部数据源和工具进行无缝集成。MCP采用客户端-主机-服务器架构,基于JSON-RPC 2.0协议,支持有状态连接和功能协商,允许AI模型访问文件、执行函数和处理上下文提示。
截至2025年4月,MCP已被多个AI平台和开发工具采纳,包括OpenAI、Google DeepMind、Replit、Sourcegraph等。其应用场景涵盖了软件开发、企业助手、自然语言数据访问等领域。
MCP服务器开发 许多大模型目前没有能力获取预报和恶劣天气警报。让我们使用MCP 来解决这个问题!
我们将构建一个公开两个工具的服务器:get-alerts 和 get-forecast。然后我们将服务器连接到 MCP 主机(在本例中,Claude for Desktop):
MCP本身提供了一些语言的SDK,包括:
Python
Node.js
Java
C#
Kotlin
以Java为例,要求如下:
Java 17 或更高版本
Spring Boot 3.3.x或更高版本
使用SDK可以大大简化我们的开发过程,比如JAVA里面的,我们只需要一个注解@Tool就可以搞定了。
需要添加Maven依赖:
spring-web:web开发依赖
spring-ai-starter-mcp-server:MCP服务器开发依赖1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.ai</groupId > <artifactId > spring-ai-starter-mcp-server</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-web</artifactId > </dependency > </dependencies >
我们增加一个Service类,该类有两个方法,这两个方法提供了我们上面说的两个工具的能力。
getWeatherForecastByLocation: 提供给Agent或者大模型的工具,输入参数是精度和纬度,根据经纬度获取天气预报。
getAlerts:提供给Agent或者大模型的工具,输入参数是地区,获取该地区的天气警报。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 @Service public class WeatherService { private final RestClient restClient; public WeatherService () { this .restClient = RestClient.builder() .baseUrl("https://api.weather.gov" ) .defaultHeader("Accept" , "application/geo+json" ) .defaultHeader("User-Agent" , "WeatherApiClient/1.0 (your@email.com)" ) .build(); } @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Points (@JsonProperty("properties") Props properties) { @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Props (@JsonProperty("forecast") String forecast) { } } @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Forecast (@JsonProperty("properties") Props properties) { @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Props (@JsonProperty("periods") List<Period> periods) { } @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Period (@JsonProperty("number") Integer number, @JsonProperty("name") String name, @JsonProperty("startTime") String startTime, @JsonProperty("endTime") String endTime, @JsonProperty("isDaytime") Boolean isDayTime, @JsonProperty("temperature") Integer temperature, @JsonProperty("temperatureUnit") String temperatureUnit, @JsonProperty("temperatureTrend") String temperatureTrend, @JsonProperty("probabilityOfPrecipitation") Map probabilityOfPrecipitation, @JsonProperty("windSpeed") String windSpeed, @JsonProperty("windDirection") String windDirection, @JsonProperty("icon") String icon, @JsonProperty("shortForecast") String shortForecast, @JsonProperty("detailedForecast") String detailedForecast) { } } @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Alert (@JsonProperty("features") List<Feature> features) { @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Feature (@JsonProperty("properties") Properties properties) { } @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public record Properties (@JsonProperty("event") String event, @JsonProperty("areaDesc") String areaDesc, @JsonProperty("severity") String severity, @JsonProperty("description") String description, @JsonProperty("instruction") String instruction) { } } @Tool(description = "Get weather forecast for a specific latitude/longitude") public String getWeatherForecastByLocation ( double latitude, // Latitude coordinate double longitude // Longitude coordinate ) { var points = restClient.get() .uri("/points/{latitude},{longitude}" , latitude, longitude) .retrieve() .body(Points.class); var forecast = restClient.get() .uri(points.properties().forecast()) .retrieve() .body(Forecast.class); String forecastText = forecast.properties().periods().stream().map(p -> { return String.format(""" %s: Temperature: %s %s Wind: %s %s Forecast: %s """ , p.name(), p.temperature(), p.temperatureUnit(), p.windSpeed(), p.windDirection(), p.detailedForecast()); }).collect(Collectors.joining()); return forecastText; } @Tool(description = "Get weather alerts for a US state") public String getAlerts ( @ToolParam(description = "Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY") String state ) { // 使用 RestClient 发起 GET 请求,获取指定州的天气警报信息 Alert alert = restClient.get() .uri("/alerts/active/area/{state}" , state).retrieve().body(Alert.class); return alert.features() .stream() .map(f -> String.format(""" Event: %s Area: %s Severity: %s Description: %s Instructions: %s """ , f.properties().event(), f.properties.areaDesc(), f.properties.severity(), f.properties.description(), f.properties.instruction())) .collect(Collectors.joining("\n" )); } }
再通过MCP提供的MethodToolCallbackProvider 工具类来将 @Tool 标记的方法转换成统一的方法,对外部提供工具。
这是因为MCP服务器规定要给外部提供统一的接口、返回值、参数。所以要转换成符合MCP规范的接口。
1 2 3 4 @Bean public ToolCallbackProvider weatherTools (WeatherService weatherService) { return MethodToolCallbackProvider.builder().toolObjects(weatherService).build(); }
接下来构建服务器,运行成功以后,会在target目录下生成一个jar包,运行该jar包应该能成功启动:
接下来我们无需启动这个jar包,直接使用Claude 桌面版客户端即可。
可以在这里下载:claude 桌面版下载
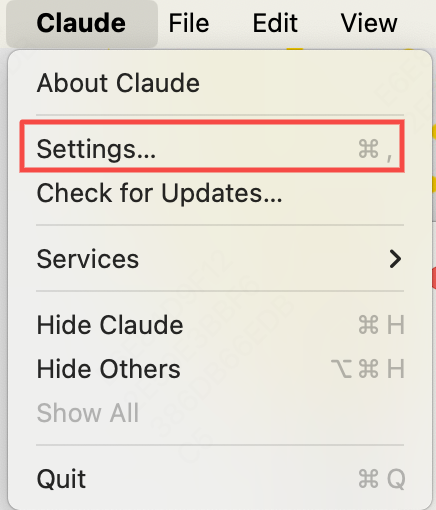
下载以后,打开应用,登陆上去,选择 Claude -》 Settings
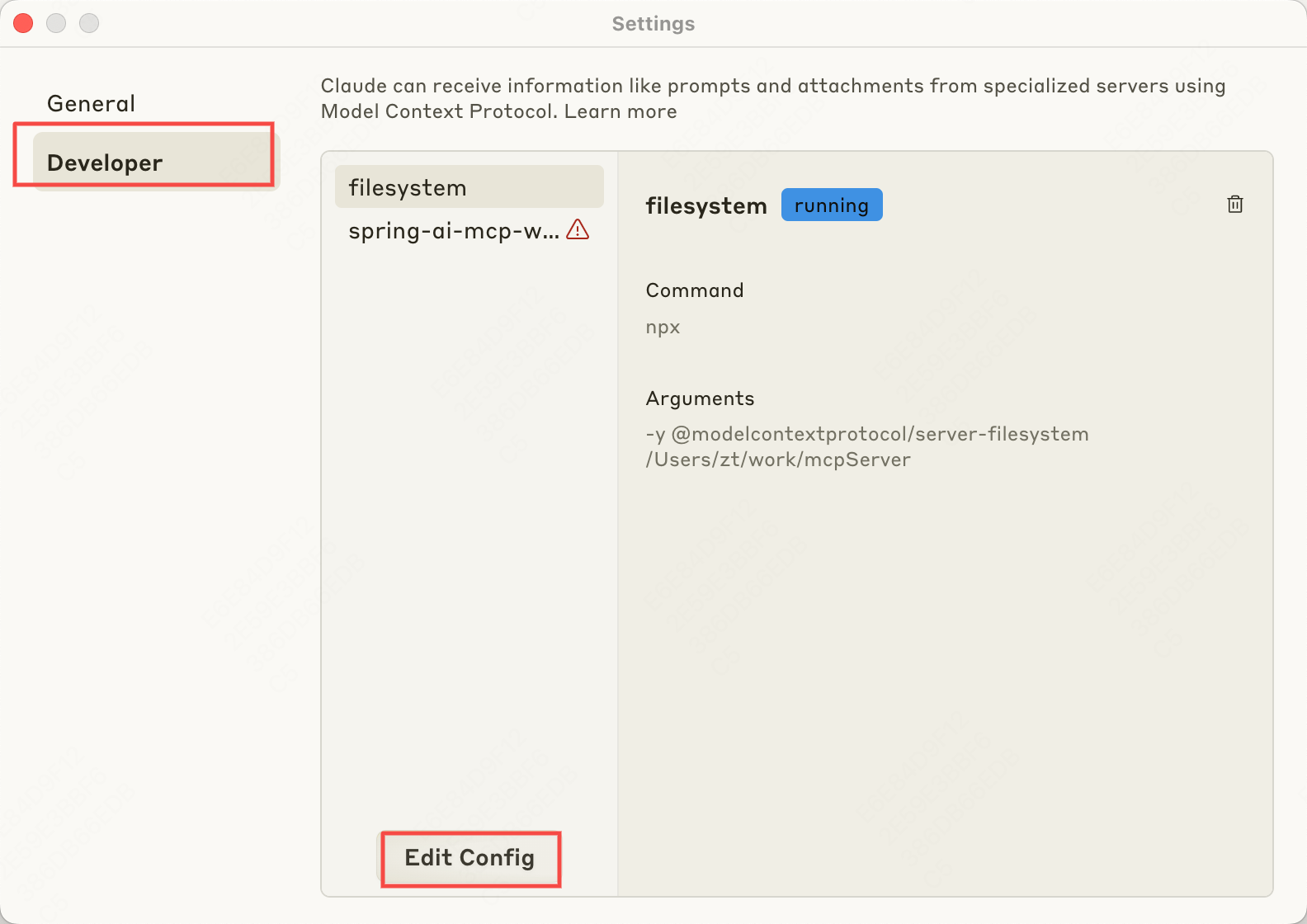
选择Developer -〉Edit Config。会自动创建一个MCP的配置文件。如果已经存在了则不会创建。
创建的配置文件名称如下:
1 claude_desktop_config.json
修改这个配置文件,内容如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 { "mcpServers" : { "spring-ai-mcp-weather" : { "command" : "java" , "args" : [ "-Dspring.ai.mcp.server.stdio=true" , "-jar" , "/mcpServer/target/mcpServer-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar" ] } } }
接下来重新启动Claude桌面版即可。在启动Claude的时候,Claude会根据上述配置文件来启动MCP服务器。启动命令类似:
1 java -Dspring.ai.mcp.server.stdio=true -jar /mcpServer/target/mcpServer-0.0 .1 -SNAPSHOT.jar
如果通过jps命令,可以看到jar包启动成功。
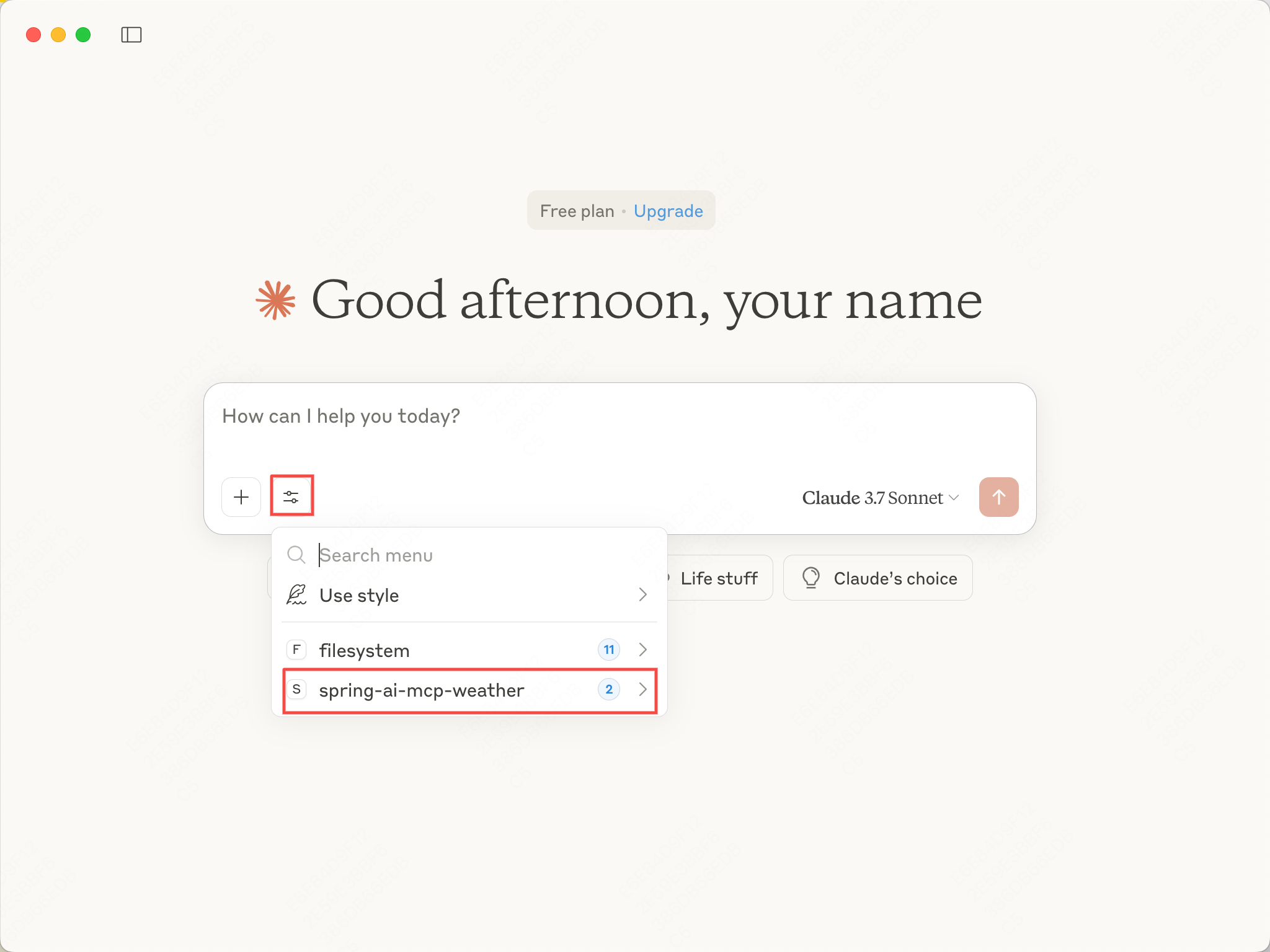
在Claude桌面版上可以看到我们刚刚配置的MCP服务器名称和提供的工具。
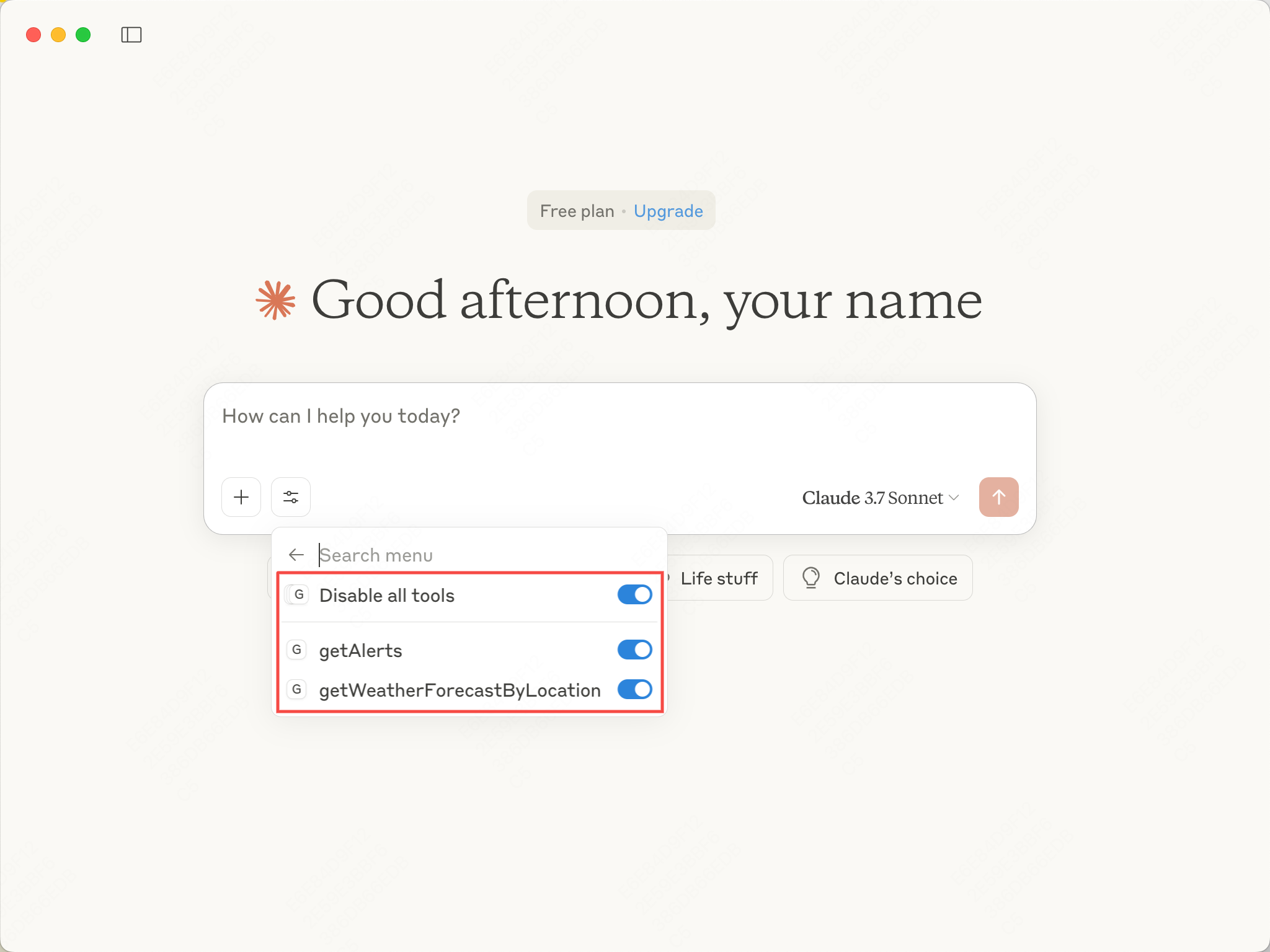
可以自主启用和禁用工具。
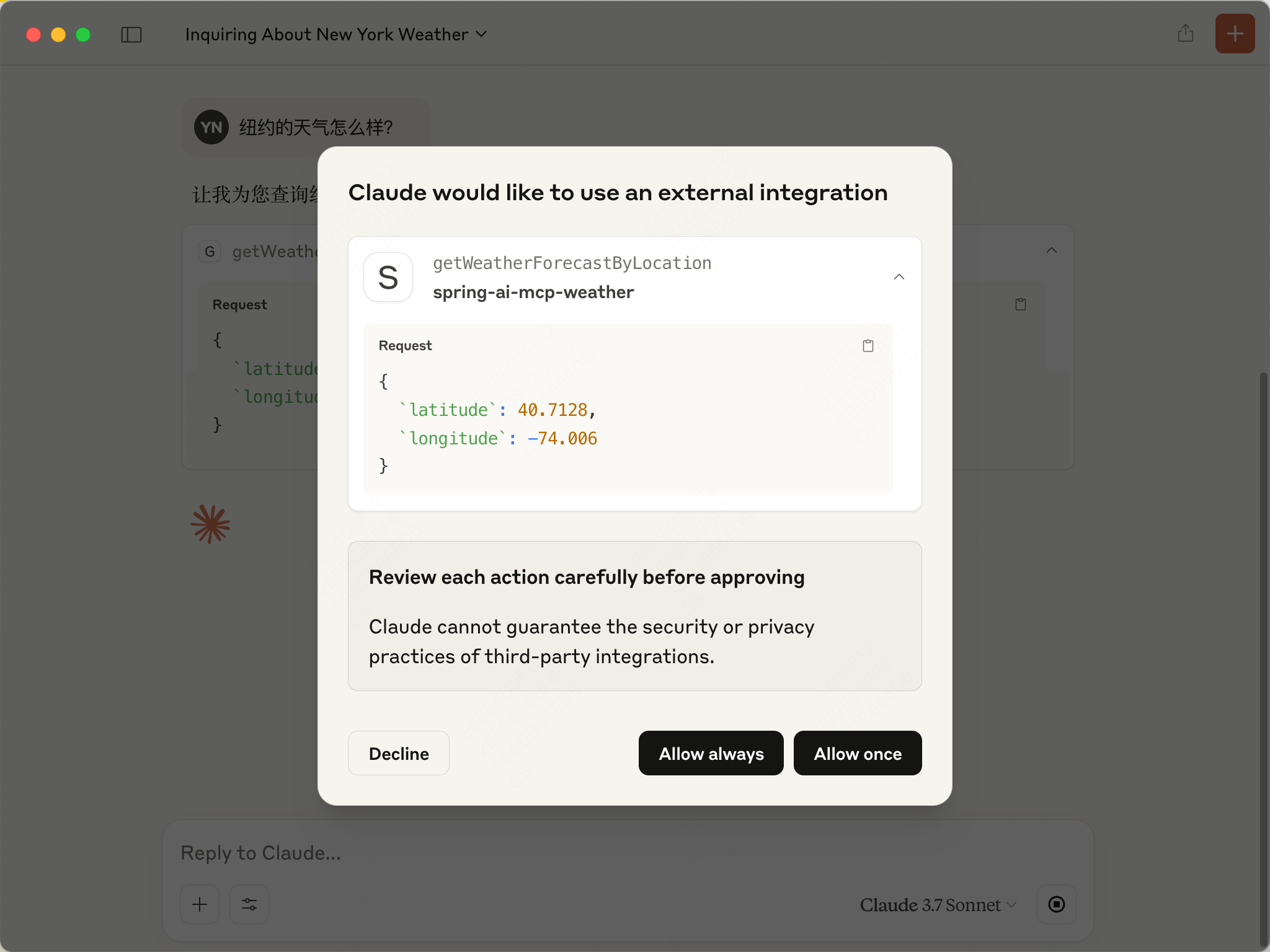
接下来我们和Claude大模型交流的时候,大模型会自己判断需不需要调用工具,调用哪个工具,如何调用。当调用的时候,会让你进行确认。
来试试输入:
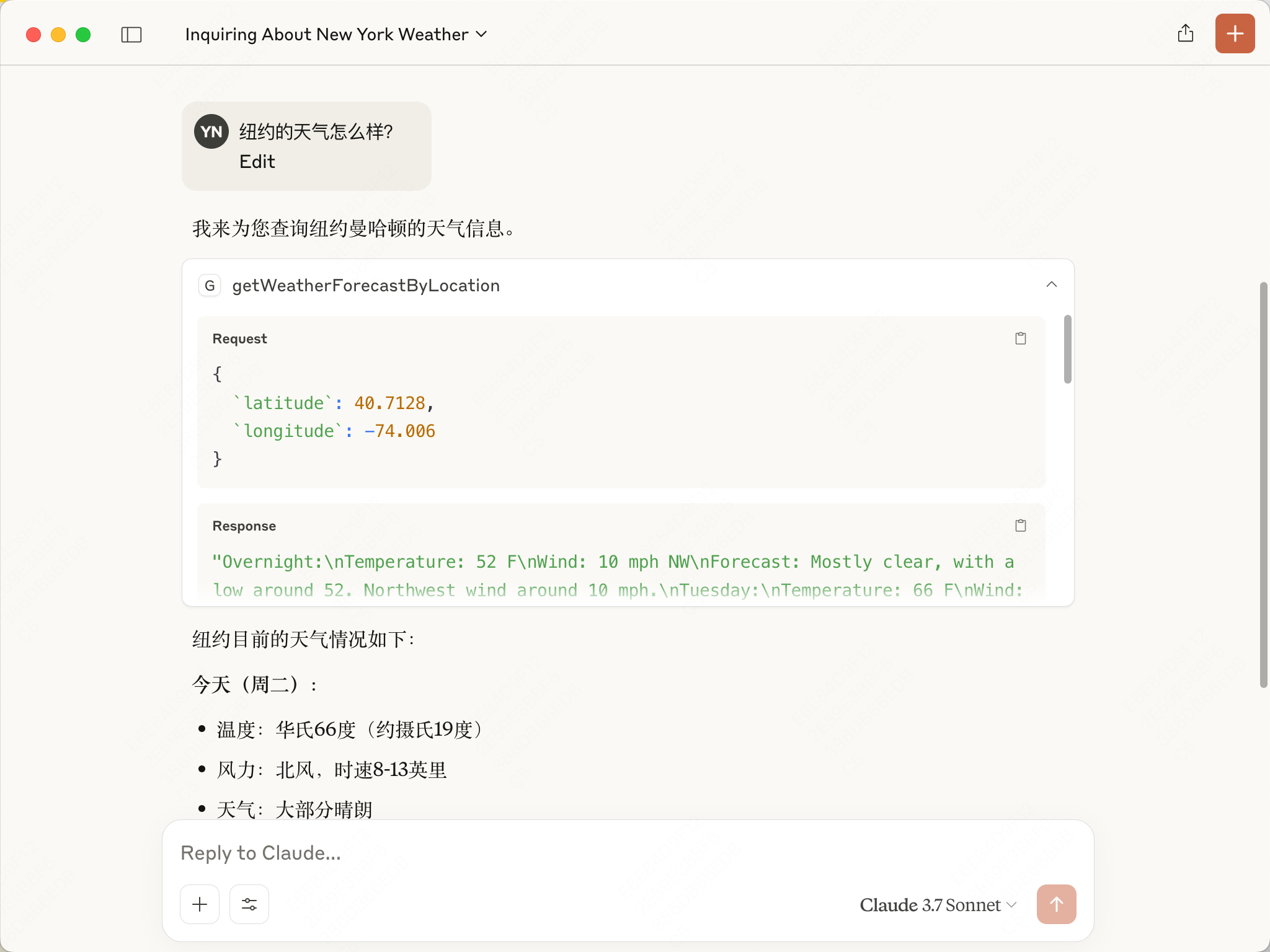
可以看到大模型自己调用了我们的工具,并展示了输入输出。
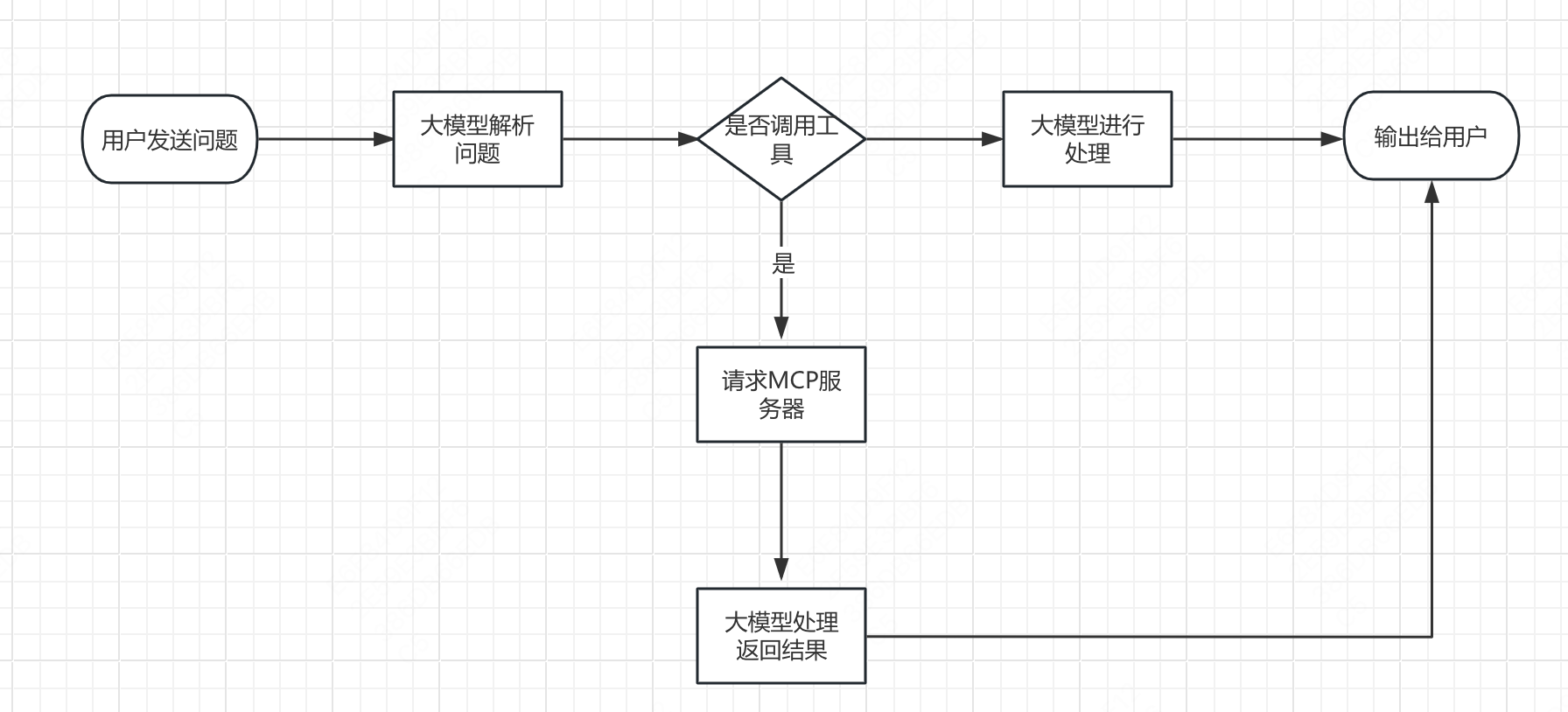
看到这里我们可以得出MCP+大模型的运行流程图。
日志 如果需要查看日志信息,可以到如下目录:~/Library/Logs/Claude
有多个文件:
mcp.log : 包含了MCP所有的日志
mcp-server-xxxxx.log: 一个MCP服务一个日志文件,记录了这个服务相关的所有日志
总结 我们主要介绍了MCP的概念,MCP的通信协议、通信方式、生命周期。MCP到底是什么东西,实现了哪些内容,使用场景以及为什么要使用MCP。
文末福利
关注我发送“MySQL知识图谱”领取完整的MySQL学习路线。